
Hair loss is a common concern for many people, affecting self-esteem and confidence. Fortunately, advances in medical technology have led to various hair restoration methods, one of which is Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT). FUT is a well-established hair transplant technique that has helped countless individuals regain a fuller head of hair. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the details of FUT, covering its procedure, benefits, risks, recovery, and more to help you make an informed decision if you’re considering this approach to combat hair loss.
Section 1: Understanding FUT
What is FUT?
Follicular Unit Transplantation, commonly known as FUT, is a surgical hair restoration method designed to address moderate to severe hair loss. FUT involves the removal of a strip of hair-bearing scalp from the donor area, usually the back of the head, where hair is genetically resistant to balding. This strip is then dissected into individual follicular units containing 1-4 hairs each.
How Does FUT Work?
The FUT procedure consists of several key steps:
Donor Area Preparation: Before the surgery, the surgeon will mark the donor area and sterilize it. The donor area is carefully selected to ensure the extracted hair will match the recipient area’s hair type and characteristics.
Anesthesia: Local anaesthesia is administered to the donor area, ensuring that the patient feels minimal to no discomfort during the procedure.
Strip Removal: A strip of scalp, typically measuring around 1 to 1.5 centimeters in width and 15 to 25 centimeters in length, is excised from the donor area. The wound is then sutured or stapled, leaving a linear scar.
Follicular Unit Dissection: The harvested strip is carefully dissected into individual follicular units under a microscope. Each follicular unit is handled with precision to preserve its integrity.
Recipient Area Creation: Tiny incisions are made in the recipient area, where hair loss is apparent. These incisions are strategically placed to mimic the natural hair pattern.
Follicular Unit Implantation: The dissected follicular units are then transplanted into the recipient area, with the surgeon paying close attention to the angle and direction of the implanted hairs to ensure a natural appearance.
Dressing and Recovery: Once the grafts are in place, the recipient area is dressed, and the patient is given post-operative care instructions.
Who is an Ideal Candidate for FUT?
FUT is suitable for individuals experiencing moderate to severe hair loss, where a larger number of grafts are required. Ideal candidates should have good donor area hair density, texture, and quality. It’s important to consult with a qualified hair transplant specialist who can assess your suitability for the procedure.
Section 2: Advantages of FUE
FUE offers several compelling advantages that contribute to its popularity among patients seeking hair restoration:
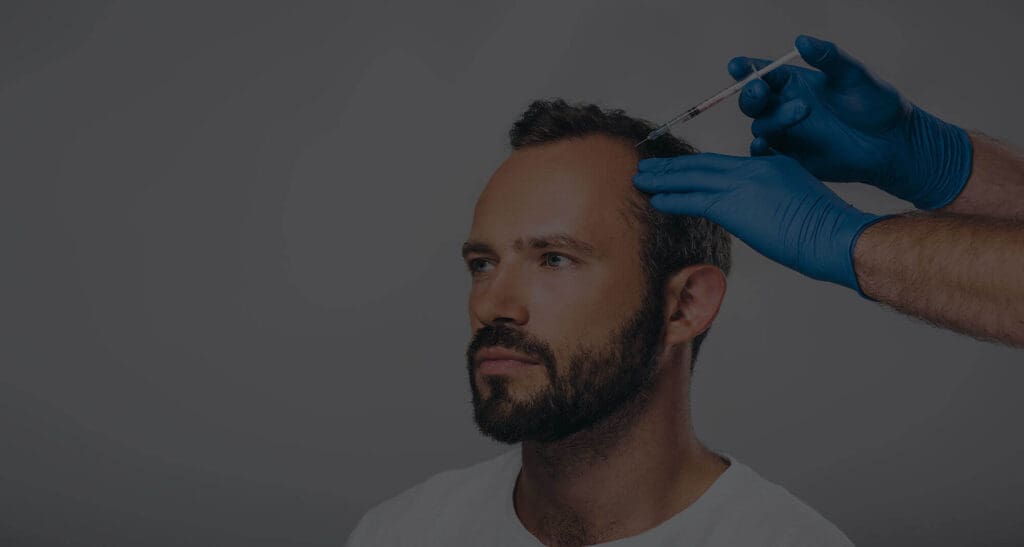
No Linear Scar: One of the most significant advantages of FUE is the absence of a linear scar in the donor area. Instead, it leaves tiny, round scars that are less noticeable, allowing patients to wear shorter hairstyles with confidence.
Minimally Invasive: FUE is a minimally invasive procedure, which means less tissue disruption, reduced bleeding, and faster healing. Patients experience less post-operative discomfort and can often resume their normal activities sooner.
Versatility: FUE is versatile in terms of the recipient area, allowing for transplantation not only on the scalp but also on areas like the eyebrows, beard, and body, making it a suitable choice for a wide range of patients.
Natural-Looking Results: The precision of FUE, coupled with the ability to extract and transplant individual follicular units, results in natural-looking hair restoration. The transplanted hair grows in the same pattern as the surrounding native hair.
Minimal Post-Operative Care: Patients who undergo FUE generally require less post-operative care than some other hair transplant methods. This includes fewer dressings and suture removal, making the recovery process more straightforward.
Section 3: Risks and Considerations
As with any medical procedure, it’s essential to be aware of the potential risks and considerations associated with FUE:
Limited Graft Yield: Compared to Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), FUE may yield a slightly lower number of grafts in a single session. This can be a consideration for individuals with extensive hair loss.
Longer Procedure Time: FUE may take longer than FUT, as each follicular unit is extracted individually. This can affect the duration of the procedure, as well as the surgeon’s and patient’s endurance.
Higher Cost: FUE is often more expensive than FUT due to the labour-intensive nature of the procedure. Patients should consider their budget when choosing a hair transplant method.
Overharvesting Risk: In some cases, there may be a risk of overharvesting from the donor area, potentially leading to thinning in that region. It’s crucial to have a skilled surgeon who can assess the available donor hair and avoid over-extraction.
Consultation is Key: Selecting an experienced and reputable surgeon is essential to minimize risks and ensure a successful outcome. The surgeon’s expertise significantly influences the results and the minimization of potential complications.
Section 4: Recovery and Aftercare
Post-Surgery Care:
Recovery after FUE is essential for achieving successful hair growth. Here are some key aftercare steps:

Medications: Your surgeon may prescribe antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medications to prevent infection and reduce swelling.
Rest: Resting is crucial in the days following the procedure. You should avoid strenuous physical activities and heavy lifting to prevent strain on the donor and recipient areas.
Hair Washing: Your surgeon will provide instructions on when and how to wash your hair after the procedure. Following these instructions is essential for proper healing.
Scab Care: Scabs may form in the recipient area. It’s important not to pick at them, as this can damage the newly transplanted grafts.
Follow-Up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your surgeon to monitor your progress and address any concerns.
Section 5: FUE Results
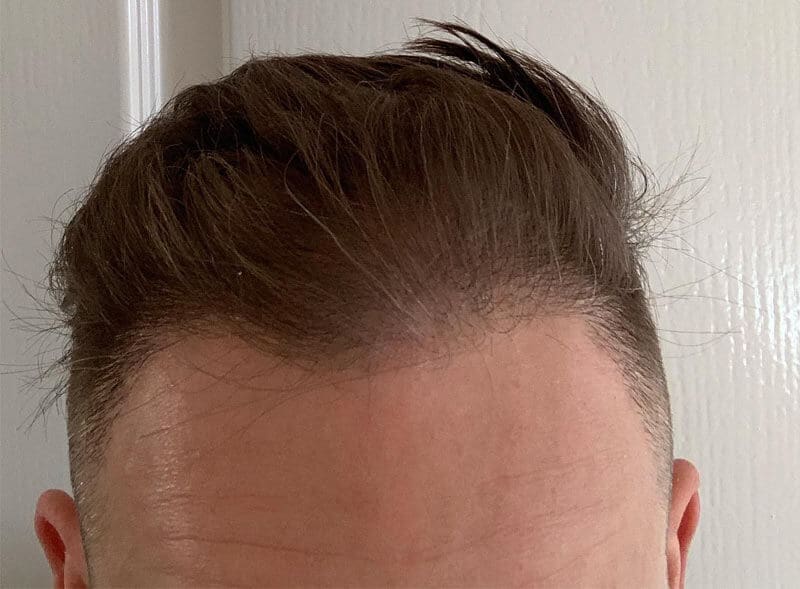
Immediate Results: After an FUE procedure, it is common for the transplanted hair to fall out within the first few weeks. This is a normal part of the process and doesn’t indicate a failed transplant. New hair growth typically begins within a few months.
Long-Term Results: Over time, the transplanted hair will continue to grow, and you will see significant improvements in hair density and coverage. The final results can take up to a year to become fully apparent.
Maintenance: While the transplanted hair is permanent, it’s important to note that the natural ageing process may cause thinning in other areas of the scalp. As a result, some patients opt for additional hair transplant sessions or non-surgical hair restoration methods to maintain their desired appearance.

Section 6 & 7: Comparing FUE with Other Methods & Conclusion
FUE is just one of several hair transplant methods available. Understanding how FUE compares to other options, such as Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Robotic Hair Transplant, can help you make an informed choice based on your specific needs and preferences.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) has gained popularity for its minimal scarring, natural-looking results, and minimally invasive nature. It’s an excellent choice for individuals with mild to moderate hair loss and those who want the flexibility of shorter hairstyles.
If you are considering FUE as a solution for your hair loss, consult with a qualified hair transplant specialist who can assess your suitability for the procedure, address your questions and concerns, and provide personalized guidance to help you achieve your hair restoration goals. By understanding the procedure, its advantages, potential challenges, and the recovery process, you can make an informed decision and take a significant step toward regaining your self-confidence and a full head of hair.




